Understanding Recurrent Pregnancy Loss (RPL)
What Causes Recurrent Pregnancy Loss?
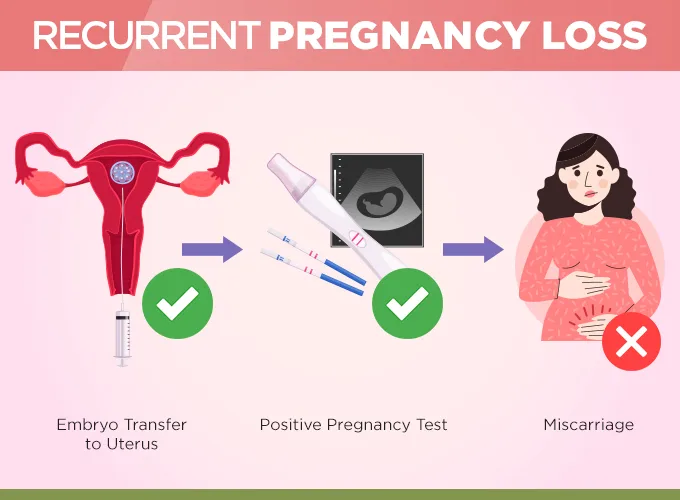
Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL), also referred to as recurrent miscarriage or
habitual abortion, is defined as the occurrence of three or more consecutive
pregnancy losses before 20 weeks of gestation. It can be caused by a variety of
genetic, anatomical, hormonal, immune, or unexplained factors.
Does Male Contribution Affect Recurrent Pregnancy
Loss?
Yes, the male factor is often overlooked but can significantly contribute to
recurrent pregnancy loss:
- Chromosomal
abnormalities in sperm are established causes of pregnancy loss.
- High levels of
sperm DNA fragmentation have been linked to unexplained RPL and are often
tested during fertility evaluation.
Do Structural Chromosomal Abnormalities Cause
Recurrent Pregnancy Loss?
Yes. One of the key structural chromosomal issues involved in RPL is translocation:
- Balanced
Translocation: A piece of one chromosome is attached to another
chromosome in a way that all genetic material is present but mislocated,
increasing the risk of miscarriage.
- These
translocations can be inherited from a parent or occur spontaneously in the
embryo (de novo).
- Carriers of such
abnormalities are often phenotypically normal, making genetic testing
essential during evaluation.
What is Sperm DNA Fragmentation?
Sperm DNA fragmentation refers to the breakage or separation of DNA strands within
sperm cells, which can have profound effects on fertility and embryo development.
- High DNA
fragmentation can interfere with embryogenesis and lead to developmental
abnormalities.
- It may increase
the risk of congenital malformations or childhood cancers.
- Fertilization
with damaged sperm can result in embryos with unstable genomes.
What is Y Chromosome Microdeletion (YCM)?
Y chromosome microdeletion (YCM) is a genetic condition caused by missing gene
segments on the Y chromosome. It is often found in men with low sperm count or
infertility.
- Many men with
YCM are asymptomatic and live normal lives.
- YCM is linked to
impaired sperm cell development and is a major cause of male
infertility.
- Genetic
counseling is advised for couples when YCM is identified during fertility
workup.
Suspect a genetic cause behind recurrent pregnancy loss? Book your consultation at Androplus
today and get expert evaluation for both partners to uncover and treat underlying
causes.